- support@husseinkey.com
- livechat
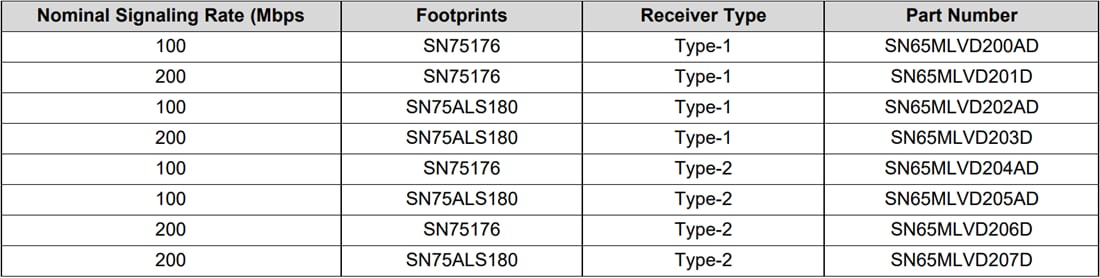
Texas Instruments MLVD20XBEVM Multipoint-Low Voltage Differential Signaling (M-LVDS) Evaluation Module (EVM) is designed to help evaluate M-LVDS devices. The SN65MLVD203B and SN65MLVD204B, in the RUM package, are installed on the circuit board. The other M-LVDS devices evaluated with this evaluation module are in the SN75ALS180 and SN75176 footprint. The use of these industry-standard footprints allows the designer to easily configure the parts into a simplex or half-duplex data bus. These are all TIA/EIA−899 MLVDS standard-compliant devices. While initially intended for half-duplex or multipoint applications, M-LVDS devices are not precluded from being used in a point-to-point or multidrop configuration. In these configurations, a distinct advantage is gained by the additional current drive provided by an M-LVDS driver.
Texas Instruments MLVD20XBEVM has been designed with the individual driver and receiver section (U1) on one half of the board and the transceiver section (U3) on the other half in the RUM package. U2 and U4 are uninstalled by default but can be installed if evaluating the supported devices. The evaluation module as delivered incorporates one 100Ω termination resistor at each driver output, receiver input, and transceiver I/O. This feature allows the user to evaluate a single driver, receiver, or transceiver, connected on the same evaluation module while not having to deal with a transmission line or additional I/Os. The evaluation module has an additional, uninstalled 100Ω termination resistor at each driver output, receiver input, and transceiver I/O that can be installed depending on the desired configuration. Additionally, each receiver output will be one-tenth of the actual value if measured at the SMA connector due to the 453Ω resistor in series with the output. The resistor is installed as a current limit for termination into a 50Ω load.
Jumpers are included to allow the two sections of the evaluation module to either share the same power and ground or be run off of independent supplies. Ground shifts or common-mode offsets can be introduced by the removal of these jumpers and using separate power supplies.