- support@husseinkey.com
- livechat
Wi-Fi® 6 is growing in demand because it is accessible even in crowded environments. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) set up the standard IEEE 802.11ax for Wi-Fi 6. Its use is expected for public Wi-Fi in extremely crowded locations, such as stations and airports. Wi-Fi 6 offers enhanced maximum transmission speed through modulation (1024QAM) and orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA), a technology that effectively assigns packets to multiple users. However, the modulation (1024QAM) is weak against noise, and the importance of noise suppression measures may increase compared to conventional standards.
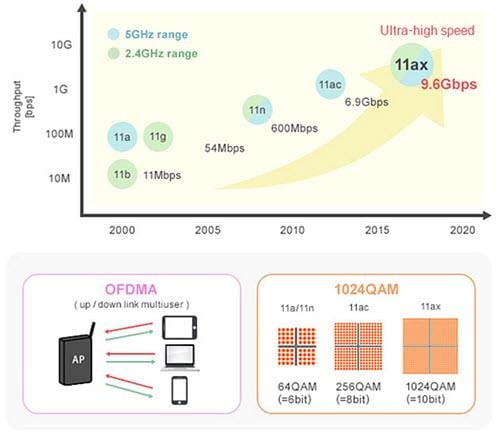
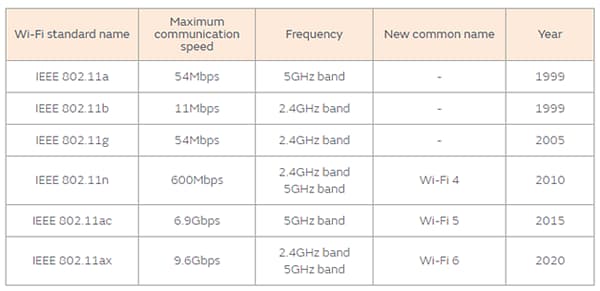

Noise issues for Wi-Fi 6 may be caused by the deterioration of transmission and reception characteristics.
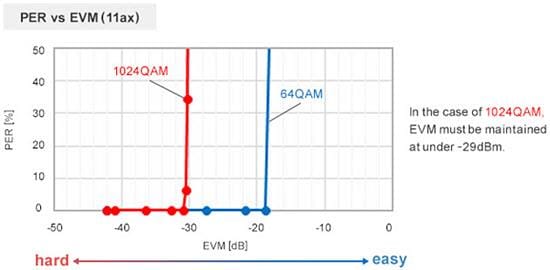
EVM is a parameter that indicates transmission characteristics. It is designed so the EVM stays below -35dB in terms of standard. It is thought ambient noise can cause deterioration in EVM value. Murata performed measurements as shown in the EVM Allowable Value Diagram (below) using a Wi-Fi 6 module to check how much EVM deterioration is acceptable in a 1024QAM communication.
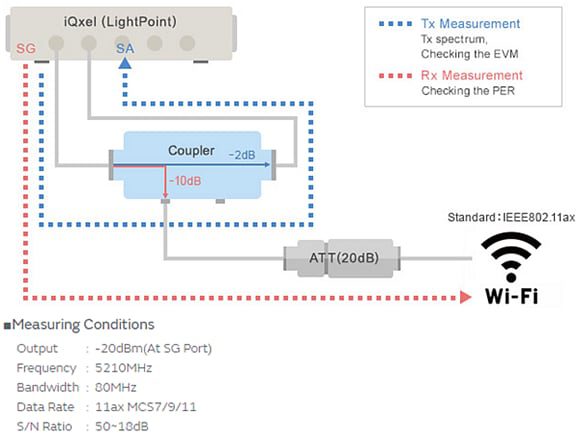

The following diagram (Figure 1, below) is the measurement result of PER vs. EVM. Murata discovered the EVM had to be under -29dBm if 1024QAM, when the standard that meets the communication quality, is under 10% PER (packet error rate).
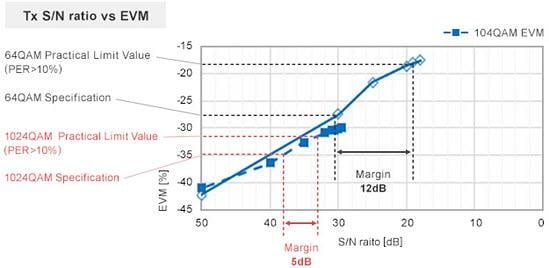
The relationship of S/N ratio between EVM and transmission waveform at this time is indicated in the second diagram (Figure 2, below). Murata found that communication becomes difficult if the S/N ratio deteriorates by 5dB for 1024QAM even if the design satisfies EVM -35dBm, a value that conforms to the standard.
The necessity to implement noise suppression measures increases since the condition is harsher compared to when the required margin was 12dB in 64QAM. The noise to consider may include BLUETOOTH® module signals, high-speed I/F signals, and DC-DC converter noise.


Noise Entry in the 5GHz Band
Wi-Fi 6 is compatible with 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, but when noise (DC-DC converter switching noise, etc.) in the 0.1GHz to 1GHz range is applied to the front end of the 2.4GHz band, third-order intermodulation distortion that interferes with the 5GHz band occurs (Figure 3, below).
Communication disturbances occur if this is transmitted to the front end of the 5GHz band through power lines, etc.
When using a base unit, communication with devices that use a 2.4GHz band Wi-Fi may be the reason. For wireless units, simultaneous use with Bluetooth may be the reason.
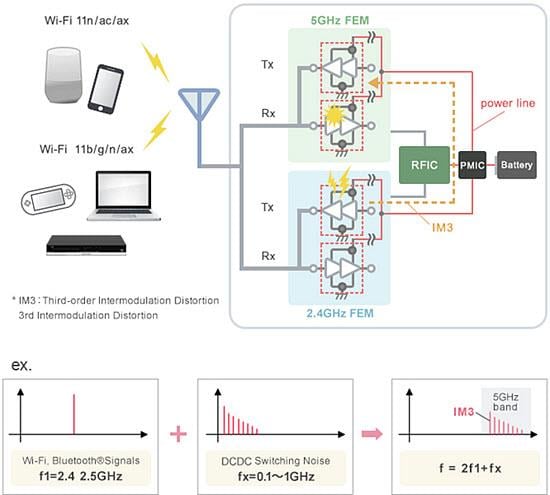

Examples of interference to the 5GHz band due to third-order intermodulation distortion
Measures Applying Noise Filters that Support the 5GHz Band
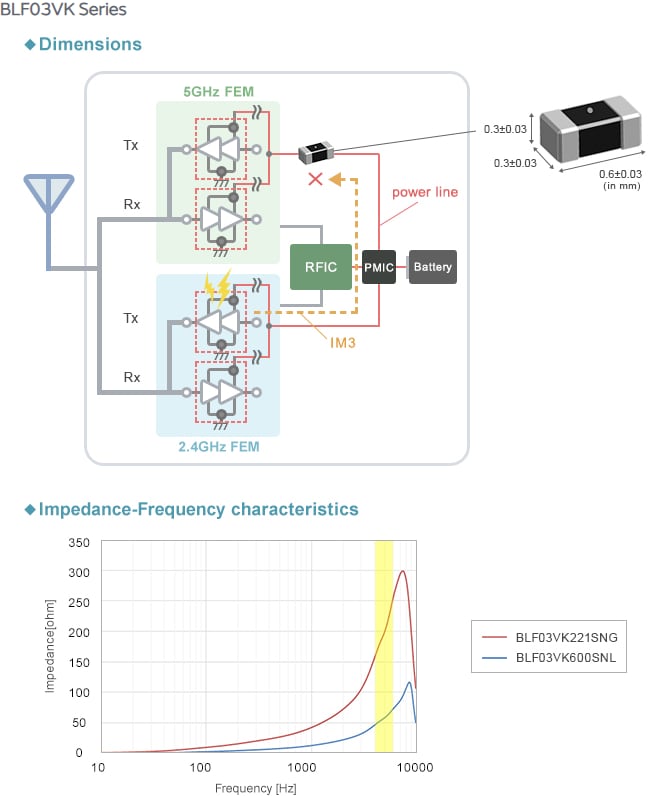
A noise filter that supports the 5GHz band is applied to prevent noise entry into the 5GHz band. Murata’s BLF03VK is a noise filter designed for the effective removal of noise in the 5GHz band.
Inserting the BLF03VK series into the power line (Figure 4, below) can prevent third-order intermodulation distortion from flowing into the front end of the 5GHz band.

Noise that Interferes with Wi-Fi from High-Speed Interfaces
Equipping high-speed interfaces can also lead to reception sensitivity deterioration.
As Wi-Fi communication becomes faster, the speed of internal data transmission interfaces will also go up, and frequencies that interfere with Wi-Fi signals will also be processed. For this reason, PCI Express signals are radiated and the 2.4GHz band Wi-Fi reception sensitivity deteriorates.
Also, because of the popularity of USB Type-C connectors, support for USB 3.1 has progressed, and due to the USB 3.1 having a signal frequency close to the 2.4GHz band, there are examples that lead to Wi-Fi reception sensitivity deterioration.
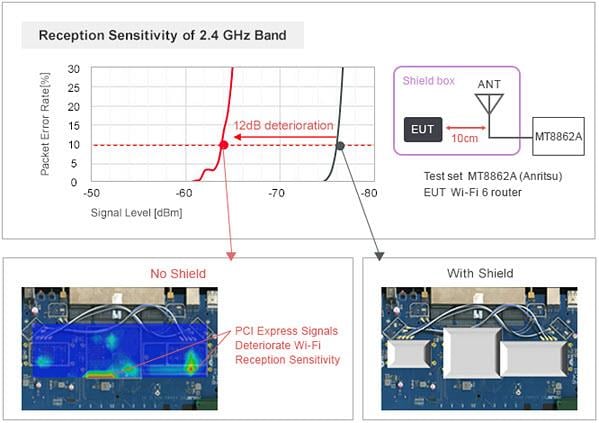

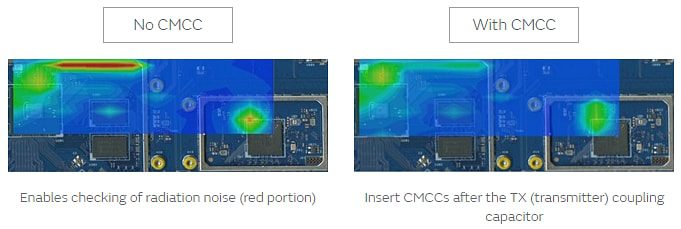
Inserting a noise filter into the signal line that does not affect the signal waveform
A noise filter is inserted on the interface signal line to eliminate noise that interferes with Wi-Fi from high-speed interfaces. However, because these interfaces use high-speed signals, users are required to select those that do not affect signal waveforms.
In principle, common mode choke coils/common mode noise filters (CMCC) do not affect differential signals. But because there are differential mode impedances in actual products to some extent, users are required to select applicable parts.

• The 1024QAM modulation method applied to Wi-Fi 6 is easily influenced by noise.
• Because Wi-Fi 6 is a dual-band structure with 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, along with the third-order intermodulation distortion that occurs in the 2.4GHz band, this results in the deterioration of the reception sensitivity of the 5GHz band. Measures can be taken by inserting the BLF03VK series into the power line.
• Wi-Fi sensitivity decrease occurs if high-speed interfaces are installed. Measures can be taken by using common mode choke coils/common mode noise filters that support high-speed signals on the high-speed interface signal line.
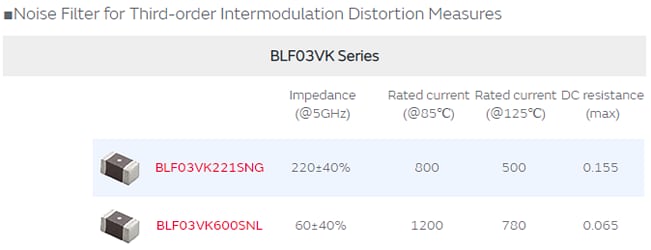

View BLF03VK221SNGD Ferrite Bead
View BLF03VK600SNLD Ferrite Bead
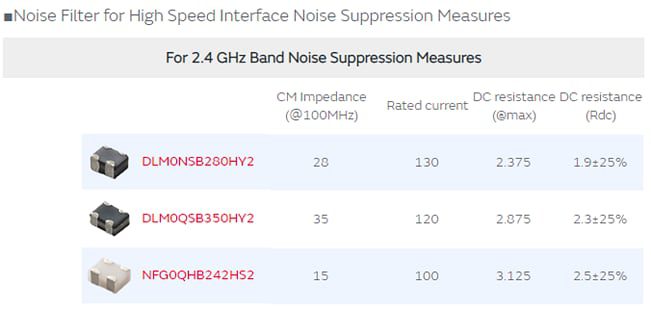

View DLM0N5B280HY2 Common Mode Choke Coil/Noise Filter
View DLM0Q5B350HY2 Common Mode Choke Coil/Noise Filter
View NFG0QHB242H52 Common Mode Noise Filter
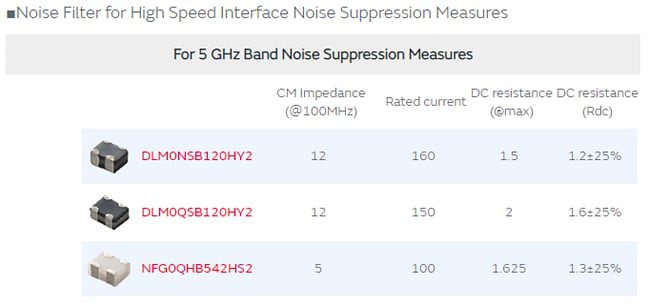

View DLM0N5B120HY2 Common Mode Choke Coil/Noise Filter
View DLM0Q5B120HY2 Common Mode Choke Coil/Noise Filter
View NFG0QHB542H52 Common Mode Noise Filter
Murata Community Forum provides searchable content with various discussion topics, popular blogs, and articles. The Murata broad market support team holds regular reviews to discuss open issues, allowing inquiries to be answered in a timely manner. The forum content is freely accessible to the public. However, users must log in to post questions or answers. Registration is free of charge.